|
110 likes | 391 Views Integrated Physics and Chemistry. MOTION GRAPHS. Graphs of Motion. Equations and tables are not the only way to describe relationships such as velocity and acceleration. Graphs can visually describe relationships. Graphs of Motion. Speed-Versus-Time.
Share Presentation Embed Code Link Download Presentation
Download Presentation
An Image/Link below is provided (as is) to download presentation Download Policy: Content on the Website is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use and may not be sold / licensed / shared on other websites without getting consent from its author. Content is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use only. Download presentation by click this link. While downloading, if for some reason you are not able to download a presentation, the publisher may have deleted the file from their server. During download, if you can't get a presentation, the file might be deleted by the publisher.
E N D
Presentation Transcript Integrated Physics and Chemistry MOTION GRAPHS Graphs of Motion Equations and tables are not the only way to describe relationships such as velocity and acceleration. Graphs can visually describe relationships. Graphs of Motion Speed-Versus-Time On a speed-versus-time graph, the speed ,v ,of a freely falling object can be plotted on the vertical axis and time t on the horizontal axis. Graphs of Motion • The “curve” that best fits the points forms a straight line. • For every increase of 1 s, there is the same 9.8 m/s increase in speed. • Mathematicians call this linearity. • Since the object is dropped from rest, the line starts at the origin, where both v and t are zero. • If we double t, we double v; if we triple t, we triple v; and so on. • What kind of relationship is v and t? • What are v and t? Graphs of Motion • This particular linearity is called a direct proportion, and we say that time and speed are directly proportional to each other. Graphs of Motion The curve is a straight line, so its slope is constant. Slope is the vertical change divided by the horizontal change for any part of the line. Slope = ∆ y/∆x = y2-y1/ x2-x1 4.7Graphs of Motion For 9.8 m/s of vertical change there is a horizontal change of 1 s. The slope is 9.8 m/s divided by 1 s, or 9.8 m/s2. The straight line shows the acceleration is constant. If the acceleration were greater, the slope of the graph would be steeper. Graphs of Motion Distance-Versus-Time When the distance dtraveled by a freely falling object is plotted on the vertical axis and time ton the horizontal axis, the result is a curved line. What else do we called the slope of distance over time? Graphs of Motion This distance-versus-time graph is parabolic. 4.7Graphs of Motion A curved line also has a slope—different at different points. The slope of a curve changes from one point to the next. The slope of the curve on a distance-versus-time graph is speed, the rate at which distance is covered per unit of time. The slope steepens (becomes greater) as time passes, which shows that speed increases as time passes. 4.7Graphs of Motion What does a slope of a speed-versus-time graph represent?
Related More by User
Describing motion with Graphs Describing motion with Graphs. Position vs. Time Graphs. x-axis: Time y-axis: Position slope = velocity (slope = “rise” / “run”) horizontal line: at rest straight line: constant velocity positive slope = positive velocity negative slope = negative velocity curved line: acceleration. 384 views • 7 slides
Understanding Motion Graphs Understanding Motion Graphs. Speed is Distance Over Time Song. ?video_id=118880&title=Mr__D___Edmonds___Speed_Is_Distance_Over_Time_Song. Speed Equals Distance Over Time Video Clip. 608 views • 34 slides
Interpreting Graphs of Motion Interpreting Graphs of Motion. Describe, in words, the motion of the objects in the following d vs. t and v vs. t graphs. 123PHYSICS – QUIZES on straight line motion 452 views • 21 slides
Motion Graphs Motion Graphs. Describing the motion of an object is occasionally hard to do with words. Sometimes graphs help make motion easier to picture, and therefore understand. GRAPHS. • Motion is a change in position measured by distance and time. 434 views • 9 slides
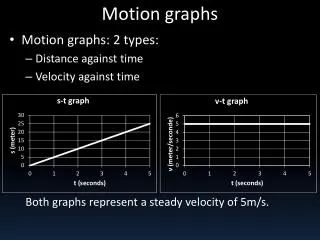
Motion graphs Motion graphs. Motion graphs : 2 types: Distance against time Velocity against time Both graphs represent a steady velocity of 5m/s. Motion graphs. B: Deceleration. A: Standstill. C: Motion at constant speed. D: Acceleration. Motion graphs. B: Acceleration. A: Standstill. 270 views • 3 slides
Motion Graphs Motion Graphs. Describing the motion of an object is occasionally hard to do with words. Sometimes graphs help make the motion easier to picture, and therefore understand. Motion is a : change in position measured by distance and time Speed tells: us the rate at which an object moves 518 views • 15 slides
MOTION GRAPHS MOTION GRAPHS. CREATING AND INTERPRETING GRAPHS. WHAT DO WE KNOW. On the paper provided, write down everything you know about graphs and graphing. Components of the Graph R eview. X- axis and Y-axis Scale and Variables Title How do you determine Scale Maximize the graph paper . 1.29k views • 31 slides
Motion Graphs Motion Graphs. 1 Dimensional Motion. Position-time graph. The object in motion would have positive and constant velocity. Position-time graph. The object in motion would have a positive but changing velocity (acceleration). Both graphs depict an object with constant and negative slope 320 views • 17 slides
Motion Graphs Motion Graphs. Homework and Review Questions. Instructions for questions 1 and 2. For each section in the graph indicate the following: Is object moving or not? If moving, in which direction? If moving, what is the average speed, average velocity?. Question #1. 17 m. 23s. 20s. 285 views • 15 slides
Motion Graphs/Vectors Motion Graphs/Vectors. Jeff, Jason, & Allie. Terms. Velocity – Rate of change of position . Acceleration – Rate of change of velocity . Speed – Ratio of distance traveled to the time interval. Distance – Scalar quantity equal to the sum of the magnitude of the displacements. 337 views • 22 slides
Motion Graphs Motion Graphs. Interpret The Graph Below:. The graph shows an object which is not moving (at rest). The distance stays the same as time goes by because it is not moving. Interpret The Graph Below:. Interpret The Graph Below:. 691 views • 29 slides
Motion Graphs Motion Graphs. Distance and Displacement. Distance is a scalar quantity! is how far something has moved. is measured in metres etc. Displacement is a vector quantity. is how far an object has moved from its starting point and in what direction. 426 views • 30 slides
Motion Graphs Review Motion Graphs Review. Interpret The Graph Below:. Interpret The Graph Below:. The graph shows an object which is not moving (at rest). The distance stays the same as time goes by because it is not moving. Interpret The Graph Below:. Interpret The Graph Below:. 505 views • 31 slides
UNIT 1 Motion Graphs Days 7 - 10. UNIT 1 Motion Graphs. x. t. Lyzinski Physics. Day #7 * a-t graphs * “THE MAP”. UNIFORM Velocity. Speed increases as slope increases. x. x. x. x. x. x. x. t. t. t. t. t. t. t. Object at REST. Moving forward or backward. x-t ‘s. 565 views • 19 slides
Motion Graphs Motion Graphs. Motion Graphs. Pictorial representations of data (or predictions/calculations) There are two motion equations that are normally graphed Position Equation Pos f = Pos o + V o t +(1/2)at 2 (General equation) S f = S o + V o t (a = 0 so V o = V any = V) 595 views • 18 slides
Representing Motion in Graphs Representing Motion in Graphs. Distance – Time Speed - Time. Plotting distance against time can tell you a lot about motion. Let’s look at the axes:. Time is always plotted on the x-axis (bottom of the graph). The Further to the right on the axis, the longer the time from the start. 338 views • 15 slides
Motion Graphs Utmost Productions is an Online Company, providing website design and development, logo design, graphics design, marketing services, product photography, and videography. Visit our website to have a look at our portfolio. 101 views • 6 slides
Motion Graphs Motion Graphs. Davey Krill May 3, 2006. Overview: Project 2. MotionTestBed Framework Motion Graph for 2 motion clips Finding candidate transitions Selecting transition points Creating Transitions (linear blending) Goal / Testing / Results Project 3. Motion Framework. 185 views • 15 slides
Motion Graphs Motion Graphs. Time – Distance Graphs. Motion Graph # 1 Straight, Flat Line. As time passes, there is no change in distance; no motion. Motion Graph # 2 Straight, Increasing Line. As time passes, distance increases The change in distance in constant – no stopping & starting. 83 views • 5 slides
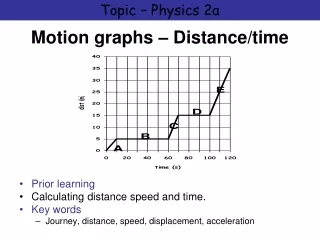
Motion graphs – Distance/time Topic – Physics 2a. Motion graphs – Distance/time. Prior learning Calculating distance speed and time. Key words Journey, distance, speed, displacement, acceleration. Exercise 1. Worksheet – Distance time/displacement time. Exercise 2. 485 views • 11 slides
Motion Graphs Motion Graphs. Interpret The Graph Below:. The graph shows an object which is not moving (at rest). The distance stays the same as time goes by because it is not moving. Interpret The Graph Below:. Interpret The Graph Below:. 386 views • 29 slides
Motion Graphs Motion Graphs. Interpret The Graph Below:. Interpret The Graph Below:. The graph shows an object which is not moving (at rest). The distance stays the same as time goes by because it is not moving. Interpret The Graph Below:. Interpret The Graph Below:. 183 views • 16 slides (责任编辑:) |