|
Step 1
Question to investigate Do cubes of exactly the same size and shape, have the same mass? Materials for the demonstration Copper cube and aluminum cube of the same volume Balance
Procedure Place the copper and aluminum cube on opposite sides of a simple balance. Expected results The copper cube will have a greater mass than the aluminum cube.
Step 2
Tell students that both cubes are exactly the same size, and both are solid with no hollow spots. Explain that the aluminum cube is made of only aluminum atoms and the copper cube is made of only copper atoms. Ask students: How can two objects, which are exactly the same size and shape, have a different mass?Help students understand that the difference in mass must have something to do with the atoms in each cube. There are three possible explanations about the copper and aluminum atoms in the cubes that could explain the difference in mass. Copper atoms might have more mass than aluminum atoms. Copper atoms might be smaller so more can fit in the same volume. Copper and aluminum atoms might be arranged differently so more copper atoms fit in the same size cube. Explain that any one of these explanations alone, or two or three together, could be the reason why the copper cube has more mass.
Give each student an activity sheet. Students will record their observations and answer questions about the activity on the activity sheet. The Explain It with Atoms & Molecules and Take It Further sections of the activity sheet will either be completed as a class, in groups, or individually, depending on your instructions. Look at the teacher version of the activity sheet to find the questions and answers.
Step 3
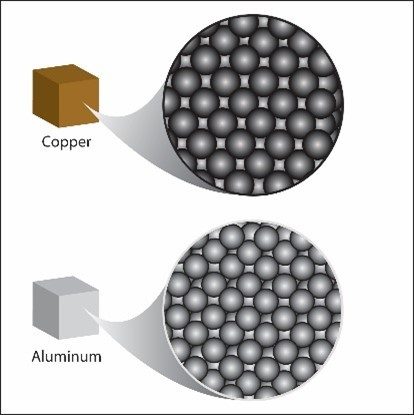
Have students turn to the illustration of copper and aluminum cubes and their atoms on their activity sheet. Show students the image Aluminum and Copper Atoms
Explain to students that the copper and aluminum atoms are arranged in the same way in their cubes. Copper atoms are a little larger than aluminum atoms. This means there are fewer copper atoms in the copper cube than aluminum atoms in the aluminum cube. But copper atoms have much more mass than aluminum atoms. So even though there might not be as many copper atoms, their extra mass makes up for it and makes the copper cube heavier than the aluminum cube of the same size and shape (volume). Note: There are different ways of measuring the size of atoms, and in close cases the results are not always in agreement. This is true with copper and aluminum. Some sources report copper as larger by some measures and some report aluminum as larger. For the purposes of this lesson, we will treat copper as the larger atom. Explain to students that this idea of how heavy something is compared to the amount of space it takes up is called density. The density of an object is the mass of the object compared to its volume. The equation for density is: Density = mass/volume or D = m/v. Each substance has its own characteristic density because of the size, mass, and arrangement of its atoms or molecules.
Step 4
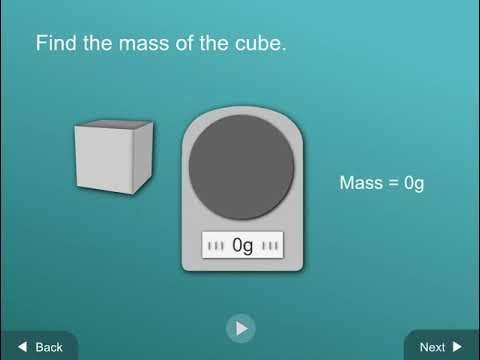
Explain to students that volume is a measure of the amount of space an object takes up. It is always in three dimensions. To find the volume of an object like a cube or a box, you measure the length, width, and height and then multiply them (V = l × w × h). If measured in centimeters, the answer will be in cubic centimeters (cm3). Note: Students often confuse volume and area. Check their understanding to make sure they know the difference. Make sure they understand that area is measured in two dimensions (length × width) with an answer in cm2. Area is a measure of the amount of surface. But volume is measured in three dimensions (length × width × height) with an answer in cm3. Volume is a measure of the entire object, including the surface and all the space the object takes up. Show the animation Cube.
Density of a Cube Lesson 3.1 Interactive
While the animation is playing, you can demonstrate the measuring process with a cube and ruler. Have students measure along with you to confirm the volume of the cubes. Volume The cubes are 2.5 centimeters on each side. Show students that in order to calculate the volume, you multiply the length (2.5 cm) × width (2.5 cm) × height (2.5 cm) to get 15.625 cm3. Rounding this number to 15.6 cm3 is accurate enough and will make the density calculations easier. Record the volume of the cube in cubic centimeters (cm3). Mass Demonstrate how to use the balance that students will be using to measure the mass of the cube. Record the mass of the cube in grams (g). Density Show students how to calculate density by dividing the mass by the volume. Point out that the answer will be in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm3).
2 Evaluate
The activity sheet will serve as the “Evaluate” component of each 5-E lesson plan. The activity sheets are formative assessments of student progress and understanding. A more formal summative assessment is included at the end of each chapter.
3 Explore
Step 5
Student groups will not need to measure the volume of the cubes. The volume of each cube is the same, 15.6 cm3 , and is given in their chart on the activity sheet. They will need to measure the mass of each of the eight different cubes and calculate their densities. Students will use their values for density to identify each cube. Note: The densities students calculate may not be exactly the same as the given densities in this chart. However, their calculations will be close enough that they should be able to identify most of the cubes. Question to investigate Can you use density to identify eight cubes made of different materials? Materials for the class Set of eight cubes of equal volume Calculator Teacher preparation Use a piece of masking tape and a permanent marker to mark the eight cubes with the letters A–H. Materials for each group Cubes marked A–H that you will share with other groups Balance that can measure in grams Calculator
Procedure The volume of each cube is given in the chart. It is 15.6 cm3. Find the mass in grams of each cube using a scale or balance. Record this mass in the chart. Trade cubes with other groups until you have measured the mass of all eight cubes. Calculate the density using the formula D = m/v and record it in the chart.
Sample Volume (cm3) Mass (g) Density (g/cm3) Material A 15.6 B 15.6 C 15.6 D 15.6 E 15.6 F 15.6 G 15.6 H 15.6
Compare the value you found for density with the given value in the chart below to identify which cube is made out of which material. Write the name of the material in your chart for cubes A–H.
Material Approximate density (g/cm3) Aluminum 2.9 Brass 8.8 Copper 9.3 Steel 8.2 PVC 1.3 Nylon 1.2 Oak 0.7–0.9 Pine or poplar 0.4–0.6
Expected results: Student values for density for each cube will not be exact, but will be close enough that they should be able to identify each of the cubes. You may notice that the approximate densities given for each cube in this lesson are slightly different than those given in the cube set. Most of this difference is probably due to the value for the volume of each cube. Since it is likely that these are 1-inch cubes, each side should be 2.54 cm. We rounded to 2.5 cm because students can make this measurement more easily.
4 Explain
Step 6
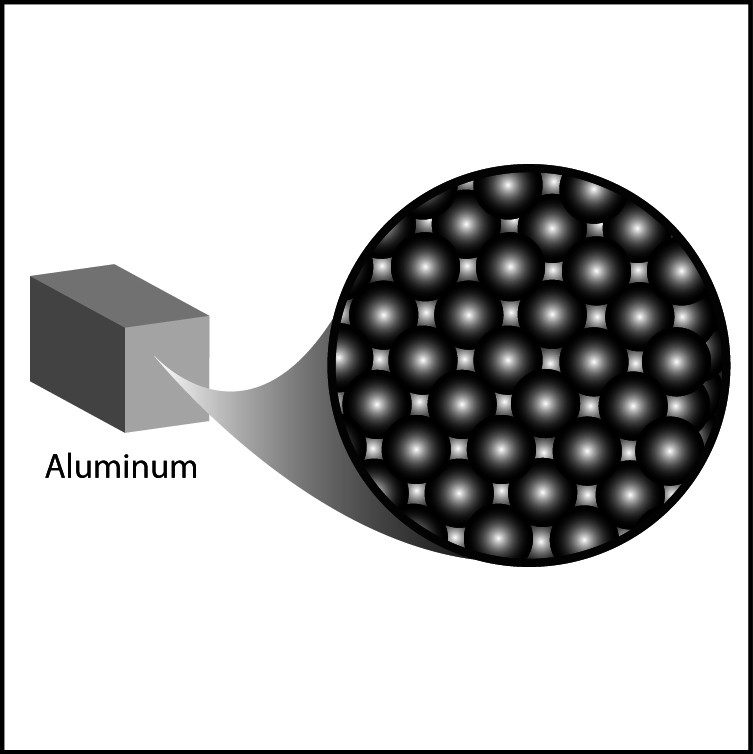
Explain to students that each substance has its own density because of the atoms and molecules it is made from. The metal, plastic, and wood cubes that students measured each have their own unique density. In general, the density of metal, plastic, and wood can be explained by looking at the size and mass of the atoms and how they are arranged. Project the image Metal.
Most common metals like aluminum, copper, and iron are more dense than plastic or wood. The atoms that make up metals are generally heavier than the atoms in plastic and wood and they are packed closer together. The difference in density between different metals is usually based on the size and the mass of the atoms but the arrangement of the atoms in most metals is mostly the same. Project the image Plastic.
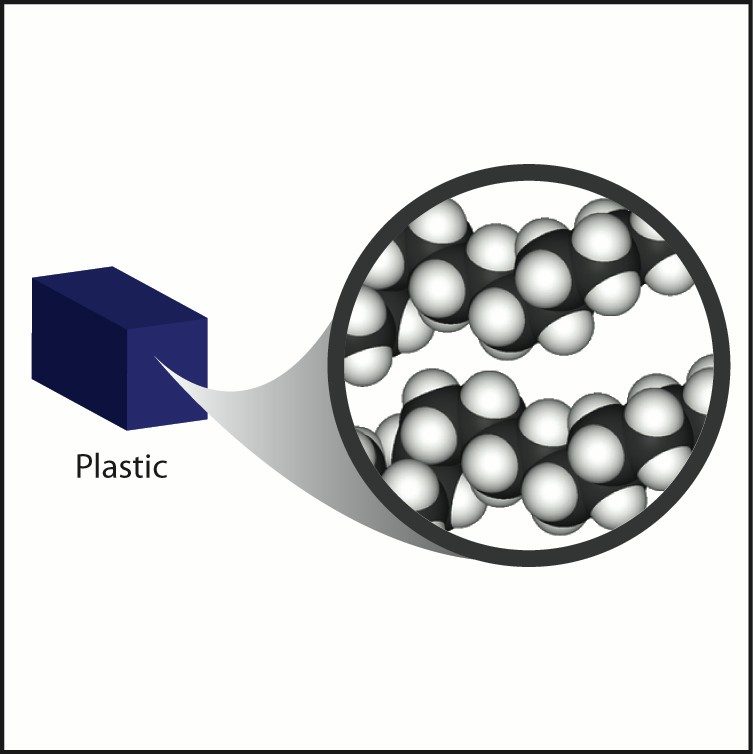
Most plastics are less dense than metal but can have similar density to wood. Plastics are made from individual molecules bonded together into long chains called polymers. These polymer chains are arranged and packed together to make the plastic. One common plastic, polyethylene, is made up of many individual molecules called ethylene which bonded together to make the long polymer chains. Like most plastics, the polymers in polyethylene are made of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
The carbon and hydrogen atoms are very light, which helps give plastics their relatively low density. Plastics can have different densities because different atoms can be attached to the carbon-hydrogen chains. The density of different plastics also depends on the closeness of packing of these polymer chains. Project the image Wood.
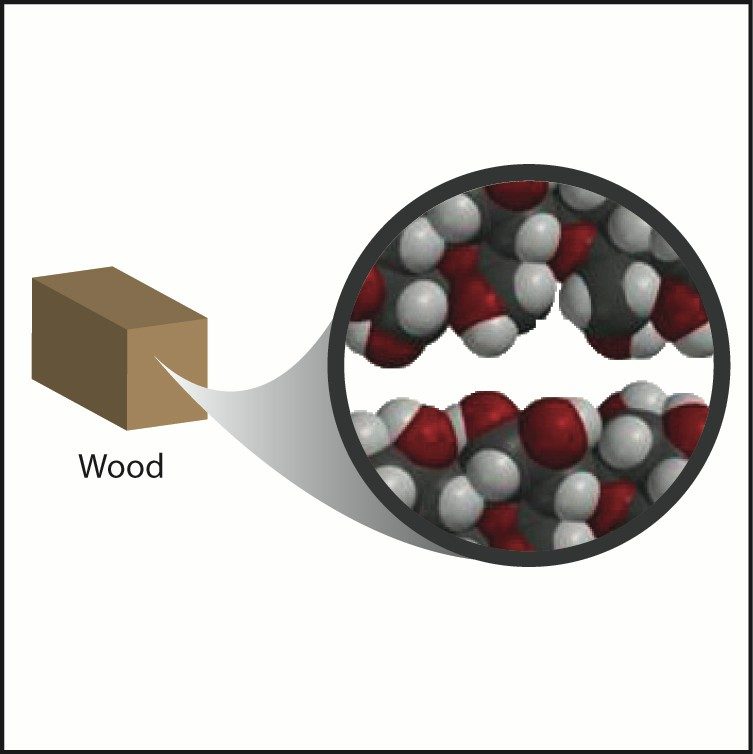
Wood is made mostly from carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms bonded together into a molecule called glucose. These glucose molecules are bonded together to form long chains called cellulose. Many cellulose molecules stacked together give wood its structure and density. In general, the density of wood and plastic are similar because they are made of similar atoms arranged in long chains. The difference in density is mostly based on the arrangement and packing of the polymer chains. Also, since wood is from a living thing, its density is affected by the structure of plant cells and other substances that make up wood.
Ask students: The size, mass, and arrangement of atoms affect the density of a substance. How might these factors work together to cause a substance to have a high density?A substance with smaller more massive atoms that are close together is going to have a higher density. How might these factors work together to cause a substance to have a low density?
5 Extend
Step 7
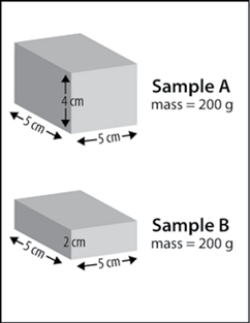
Remind students that they looked at cubes that had the same volume but different masses. Point out that their activity sheet has drawings of two blocks (Sample A and Sample B) made of different substances that both have the same mass, but different volumes.
Ask students: What is the density of Sample A?Volume = 5 × 5 × 4 = 100 cm3 What is the density of Sample B?
Hint: The size, mass, and arrangement of molecules affect the density of a substance. There are several possible answers for why sample B is more dense than sample A.
Sample B atoms might have more mass than Sample A atoms. Sample B atoms might be smaller than Sample A atoms so more can fit in the same volume. Sample B atoms might be arranged differently so more Sample B atoms than Sample A atoms fit in the same size cube. Any one of these explanations alone, or any combination, could be the reason why Sample B is more dense than Sample A. (责任编辑:) |